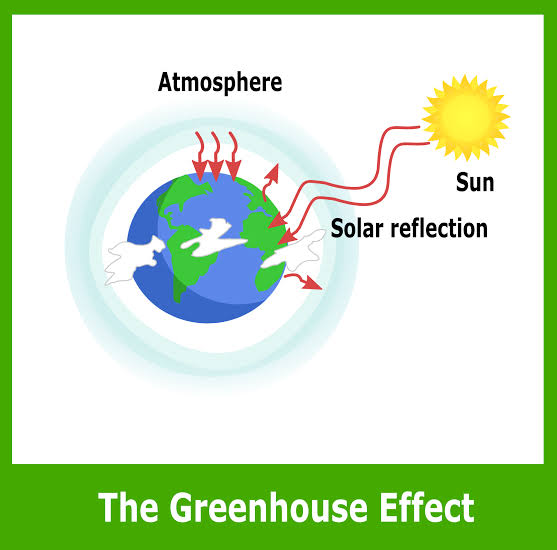
Ever wondered why the Earth is heating up? It all comes down to something called the greenhouse effect. It’s a natural process, but our actions are turning up the heat—literally.
In this article, I’ll break down what the greenhouse effect is, how greenhouse gases play a role, and why it’s fueling global warming. If you care about our planet’s future, stick around—this is something we all need to understand.
What is the Greenhouse Effect?
To put it simply, the greenhouse effect is a natural process where certain gases in our atmosphere trap heat, keeping Earth warm enough for life. The sun sends energy to our planet, and while some of it reflects back into space, most of it stays here, keeping our planet cozy.
But what traps this heat? Greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and water vapor.
Here’s how the greenhouse effect works: When sunlight reaches Earth, it warms the surface. This warmth then radiates back toward space as infrared energy. Instead of all that heat escaping, greenhouse gases absorb some of it and send it back to Earth, creating a warming effect. Without this natural process, our planet would be too cold for life as we know it.
However, human activities, like burning fossil fuels and deforestation, are pumping extra greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. This intensifies the greenhouse effect, causing global warming.
Key Greenhouse Gases
When we talk about the greenhouse effect, it’s important to know about the key greenhouse gases driving it. These gases trap heat in our atmosphere, contributing to global warming.
Here are the primary ones:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): CO₂ is the most well-known greenhouse gas. It’s released mainly through burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. Deforestation also adds to CO₂ levels since trees absorb carbon dioxide.
- Methane (CH₄): Methane is another powerful greenhouse gas, even more effective at trapping heat than CO₂. It comes from livestock digestion, landfills, and the production of oil and gas.
- Nitrous Oxide (N₂O): N₂O is less talked about but is a potent greenhouse gas. It’s mainly released from agricultural activities, especially through the use of synthetic fertilizers.
- Water Vapor: Water vapor is a natural greenhouse gas and the most abundant one. It amplifies the greenhouse effect by increasing as the planet warms, creating a feedback loop.
These greenhouse gases contribute to the greenhouse effect by absorbing heat and keeping it in our atmosphere. This process is natural, but human activities have dramatically increased the concentration of these gases, leading to an enhanced greenhouse effect and, ultimately, global warming.
How the Greenhouse Effect Causes Global Warming
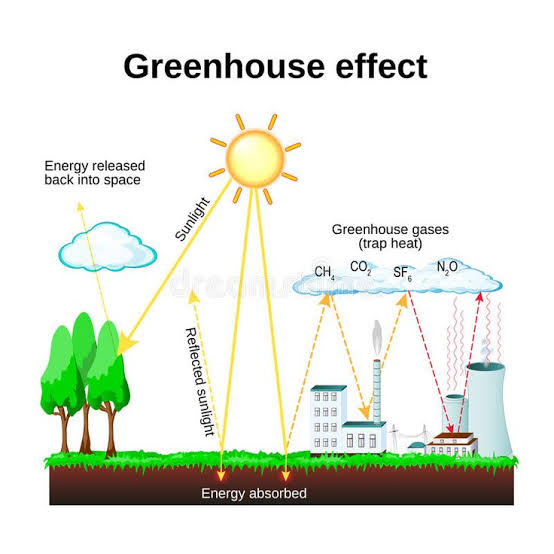
The greenhouse effect explained simply is like a blanket around Earth that keeps it warm. Think of it as Earth’s way of staying warm—like a cozy blanket that keeps the planet at a nice temperature.
Normally, this is a good thing, but when human activities add extra greenhouse gases into the mix, things start to heat up more than they should, causing global warming.
Here’s how it works: Sunlight reaches Earth and warms the surface. Normally, some of this heat would escape back into space, but greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and nitrous oxide (N₂O) trap the heat, keeping our planet at a stable temperature. This is the greenhouse effect explained simply.
However, when we burn fossil fuels for energy, clear forests, and engage in other activities, we release more of these gases into the atmosphere.
This extra buildup of greenhouse gases means more heat is trapped, which in turn raises Earth’s average temperature. This is what we mean when we talk about the greenhouse effect causing global warming.
Human activities have significantly increased the concentration of greenhouse gases since the Industrial Revolution.
For example, CO₂ levels have risen dramatically due to the burning of coal, oil, and natural gas. Methane emissions have spiked from livestock farming, landfills, and the oil and gas industry. Even nitrous oxide has increased, mainly from the use of synthetic fertilizers in agriculture.
As these gases accumulate, the enhanced greenhouse effect leads to higher global temperatures, which we experience as global warming. This warming affects weather patterns, causes ice caps to melt, and raises sea levels, among other impacts.
Want to take control of your energy use and help the planet? Switch to solar power with our top-notch, affordable solar panels! Start saving on your bills and reduce your carbon footprint today.
It’s simple—just click here to see how easy it is to make the switch and join the solar revolution. Let’s power up for a greener tomorrow!
Impact on Climate and Environment
Here’s how the greenhouse effect impacts our climate and environment—and why this matters more than ever.
1. Rising Global Temperatures:
The greenhouse effect explained in simple terms is like Earth’s natural heating system. Normally, it keeps our planet warm enough for life. But when greenhouse gases like CO₂ and methane get out of balance, this system starts overheating.
As a result, global temperatures have been steadily rising. Scientists describe this as global warming, and it’s happening at a rate that’s too fast for many ecosystems to adapt.
2. Shifting Weather Patterns:
As the Earth warms, we’re seeing dramatic changes in weather patterns. Winters are becoming shorter, summers hotter, and storms more intense.
What’s happening here is that the energy trapped by greenhouse gases doesn’t just warm the planet—it also drives more extreme weather.
For example, hurricanes are becoming stronger because warmer oceans provide more fuel for these powerful storms. Meanwhile, droughts are becoming longer and more severe, putting stress on water supplies and agriculture.
3. Rising Sea Levels:
Another consequence of the greenhouse effect is rising sea levels. As global temperatures increase, polar ice caps and glaciers are melting at alarming rates. This meltwater flows into the oceans, causing sea levels to rise.
For people living in coastal areas, this is a huge threat. Higher sea levels mean more frequent and severe flooding, especially during storms. This not only damages property but also leads to the loss of critical habitats for wildlife.
4. Ecosystems Under Threat:
The impact of the greenhouse effect on the environment doesn’t stop there. Ecosystems around the world are feeling the strain. Coral reefs, often referred to as the “rainforests of the sea,” are bleaching and dying due to warmer waters.
Forests are struggling with more frequent wildfires and pest outbreaks. And species that can’t adapt quickly enough to the changing conditions are at risk of extinction.
But it’s not just remote ecosystems that are affected. The greenhouse effect and global warming are also changing the environments we rely on for food, water, and shelter.
For instance, shifts in growing seasons are disrupting agriculture, leading to food shortages in some parts of the world.
Mitigation and Solutions to the Greenhouse Effect Problem
Here’s how we can tackle the greenhouse effect and make a positive impact on our planet.
1. Shift to Renewable Energy:
One of the most effective ways to cut greenhouse gas emissions is to switch from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower. These alternatives produce little to no greenhouse gases, helping to stabilize our climate.
Want to take control of your energy use and help the planet? Switch to solar power with our top-notch and affordable solar panels! Start saving on your bills and reduce your carbon footprint today.
It’s simple—just click here to see how easy it is to make the switch and join the solar revolution. Let’s power up for a greener tomorrow!
2. Improve Energy Efficiency:
Using energy wisely reduces the amount of fossil fuels needed leading to better insulation in homes and more efficient appliances and vehicles. This means fewer emissions and less impact on global warming.
3. Adopt Sustainable Practices:
Practices like reducing waste, recycling, and supporting sustainable agriculture can significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions. For example, planting trees and preserving forests help absorb CO₂ from the atmosphere.
4. Promote Public Transportation and Electric Vehicles:
Reducing our reliance on cars and encouraging the use of public transport or electric vehicles can cut down on emissions from burning fossil fuels.
5. Support Climate Policies:
Advocating for and supporting policies that aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions at local, national, and international levels is crucial. This includes agreements like the Paris Agreement, which sets targets for emission reductions globally.
Final Thoughts
So, we’ve unpacked the greenhouse effect—how it traps heat, the major gases involved, and its impact on our climate. From warmer temperatures to extreme weather, the stakes are high, but there’s a lot we can do to make a difference.
Why not start with something simple? Switching to solar power is a great first step. It’s easy, effective, and helps reduce your carbon footprint. Check out our solar panels and see how you can start saving money while also helping the environment.
Every small action counts. Let’s take these steps together and make a positive impact on our planet!