- This article is centered on Pineapple, with the botanical name Ananas comosus.
It is a tropical herbaceous perennial crop with edible fruit and the most economically significant plant in the family Bromeliaceae.
It has many native names and in Nigeria, it is called ‘Akwu Oru’ in Igbo, Ope Oyibo in Yoruba and Eyop Mbakara in Ibibio.
Pineapple is native to South America, where it has been grown for many centuries.
Its origin can be traced to the Parana–Paraguay River drainages between southern Brazil and Paraguay.
Little is known about domestication, but it spread as a crop throughout South America, and it eventually reached the Caribbean, Central America, Europe, and Africa.
Pineapple flowers once and produces a single pineapple or at most two. After fruiting, then dies off.
However, each fruit comes with a sucker that can be planted again. Pineapple is mostly planted by its sucker.
The most commonly grown variety in Nigeria and Africa is called smooth cayenne.
The variety is used predominantly in Africa and the world because it is quite resilient and productive.
Some pineapple species are grown as ornamentals for color, novel fruit size, and other aesthetic qualities.
Nutrient Composition Of Pineapple
Pineapple is rich in manganese and vitamin C. Nutrient Amounts per 100g is as follows:
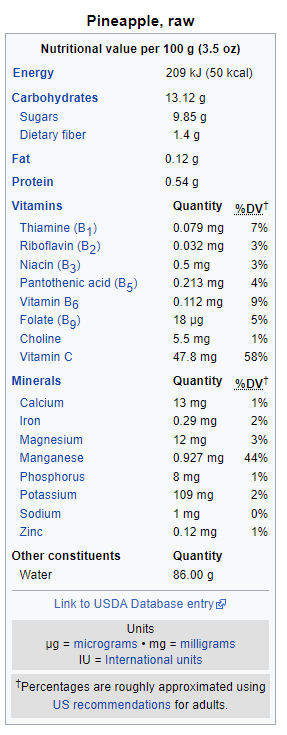
Source: Wikipedia
Medicinal Properties Of Pineapple
Below are some of the health benefits of pineapple.
- The antioxidants in pineapple fight against diseases and reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
- Pineapples ease digestion due to the presence of bromelain in them. Bromelain breaks down protein which may also aid digestion.
- Eating pineapple helps reduce the risk of cancer due to compounds that reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which are related to cancer.
- Pineapple contains vitamins, minerals, and enzymes like bromelain that may help to boost immunity and suppress inflammation.
- It helps to ease the symptoms of arthritis
- Eating pineapple after surgery or strenuous exercise can help the person recover.
Fruiting and Yield Information Of Pineapple
Pineapple takes up to 18-24 months to

grow from sucker to ready-to-consume fruit.
It takes a minimum of a year for pineapple seedling to grow into a mature plant and start fruiting. Then, takes another six months for the fruit to be ready for consumption.
Pineapple yields a maximum of two fruits per stand. The majority of the stands yield just one fruit.
Each fruit comes with a new sucker that you can plant. After fruit maturity and harvesting, the plant dies off.
Pineapple may produce offsets once it starts flowering. Offsets are small plants growing off the main plants.
They can grow into mature plants and produce their flowers and fruits as well.
Do not temper with offsets, until after harvesting the fruit from the mother plant to avoid damaging the mother plant.
After harvesting, you can now separate the offsets from the mother plant and plant them until maturity.
Planting and Spacing Requirements Of Pineapple

This juicy fruit requires good apacing to grow well. It can be planted from either suckers or offsets.
The sucker is the leafy fruit crown from the fruit and can be plucked from the fibrous fruit core and planted.
Also, a mature pineapple plant produces offsets (baby plant) around its base or the fruit crown, which can be separated from the mother plant and planted.
A suitable planting space for pineapple is double row spacing at 60cm between rows, 30cm between plants, and about 120cm between adjacent double rows.
Ridging should preferably be done after planting the sucker 7cm to 10cm deep on a leveled ground.
Pineapples can first be planted on a nursery bed, then transplanted later to the planting bed. This is possible because they have a tiny root system.
Soil And Sun Requirements Of Pineapple
A well-drained and sandy loam soil with a soil pH between 4.5 to 6.5 are ideal for planting pineapples.
Pineapples will not thrive in a water-saturated area; hence, it requires sandy loam soil because it is loosed and allows for water movements through the soil.
Pineapple can survive prolonged dryness, but it requires even moisture with a high organic matter content for it to develop well. You should pulverize the soil to 60cm (2 feet).
The plant needs all-day sunlight and a temperature range between 65 and 85 degrees Fahrenheit to remain healthy and growing.
The plant will do well in cool times for a short period; however, prolonged cold slows growth, delays maturity, and the fruit becomes more acidic.
It requires full sunlight to produce the best fruit. Insufficient sunlight can delay foilage development and prevent flowering. The flavor of the fruit can be affected by the altitude.
Pineapple requires soil nutrients such as nitrogen, especially for the young ones, as well as Magnesium and potassium all of which are essential nutrients in pineapple growth.
Watering Requirements Of Pineapple
Pineapple require about one inch of water per week either by rainfall or artificial irrigation.
In arid areas, manual irrigation should be provided, which will cut across all watering situations from at planting and 8-12 weeks before harvest in dry seasons.
Harvesting Of Pineapple
When the bottom of the fruit slightly changes color to yellow, that’s a sign of maturity.
You may allow it to further ripen before harvesting or you may harvest at this stage and keep it at room temperature to further ripen.
Harvest the fruit with a sharp knife. Cut off the fruit from the bottom such that the fruit is not damaged and the crown is retained.
Storage And Preservation Of Pineapple
The adequate temperatures of 7 to 12°C (45 to 55°F) are recommended to store pineapples for 14 to 20 days, bearing in mind the fruits are at the color break stage.
Relative humidity of 85 to 95% is recommended. A high relative humidity significantly reduces water loss.
Ripe fruit can store for about 7 to 10 days at 7.2°C (45°F). It is best to Keep cut pineapples in the refrigerator.
Put cut fruits in an airtight container for a longer life span. You can also store pineapples for the long term, but you have to freeze them in an airtight container.
Pineapple Sucker Storage
You can store suckers in a cool, dry place at room temperature. Suckers should not be kept for very long without planting to avoid decay and spoiling.
Pests And Diseases Of Pineapple
Commonest pest and diseases affecting pineapple are:
1. Bacterial Heart Rot And Fruit Collapse
Caused by bacteria, Symptoms include water-soaked lesions on the white basal section of the leaves. It may spread to all leaves. Fruits that have been infected bring out juices, and the shell turns olive green. Cavities also form within the fruit.
Natural ways of management include removing and destroying infected fruits and avoiding the use of infected crowns for seed material to prevent the spread of the disease.
2. Butt Rot And White leaf spot
This disease is primarily caused by Fungi, symptoms include a soft black spot that begins at the area where the seed piece detaches from the mother plant.
Wet spots develop on leaves. You can manage it by storing seed material on mother plants during dry weather with good air circulation.
Avoid wounding and bruising fruits during harvest to help reduce black rots.
3. Mealybugs
Mealybugs are insects that are sometimes attracted to the pineapple plant. Plants may show symptoms of mealybug wilt, flattened oval disc-like insect covered in waxy substance on the leaves.
It can be controlled by using natural enemies such as lady beetles.
Phytophthora heart and root rot
Caused by Oomycetes, its symptoms include:
- Young leaves falling to elongate and turning chlorotic
- Terminal whorl can be easily pulled from the mother plant
- Water-soaked tissues at the base of leaves, and a foul smell.
You can manage it by using raised beds that help drain the soil. It would be best if you avoided mulch from pineapple debris.
Conclusion
Pineapple is a healthy and very tasty fruit that is safe and ideal for all ages across the globe.
Though cultivation and yield may seem long. It is usually worth the while.
